Last Updated on May 17, 2024
Are you planning to conduct business operations in China or seek partnerships with Chinese companies? If your answer is yes, chances are you’re wondering what business licenses you’ll need.
We know that complying with local regulations and requirements can be tricky, especially for foreign companies and investors entering the Chinese market for the first time. In this post, we’ll explain how to obtain a business license in China and the procedures that come along with it.
Do you need a business license in China?
The necessity of obtaining a Chinese business license depends on the trading activities the company conducts within the country. It’s a highly recommended process, especially if your brand intends to expand more thoroughly within China in the long run.
However, it’s worth noting that not every business structure must undergo a tedious business registration required by government authorities in Mainland China.
For example, if your business scope only involves selling products and services online, you can enter the market using cross-border e-commerce platforms.
While these channels require you to submit company information and other important documents, they eliminate the need to establish an actual business location within the country or the requirement of a domestic business license.

Meanwhile, foreign companies that intend to launch a website with e-commerce business activities may need to apply for an ICP commercial license. A Chinese business license is among the several requirements overseas brands must acquire for this process.
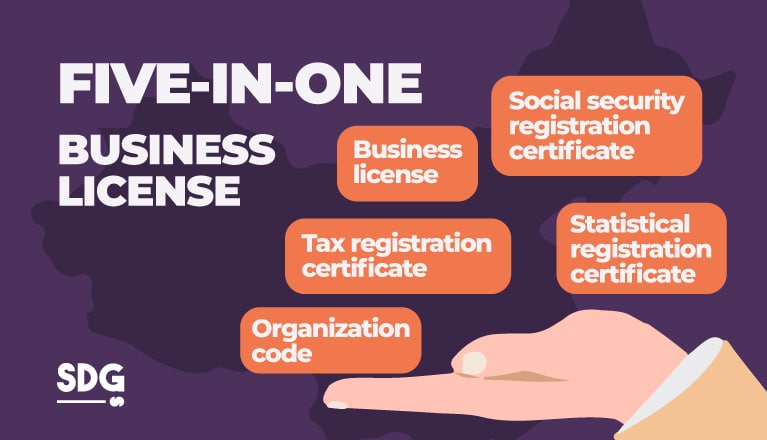
What is a Five-in-One business license in China?
The five-in-one business license is one of the fastest ways foreign companies can establish an entity and operate legally within China’s thriving business scene.
True to its name, it’s a system that combines the filing for the company’s tax registration certificate, business license, social security registration permit, organization code, and statistical registration certificate.
Before the implementation of 5-in-1 business licenses in China, non-Chinese company registration was tedious and lengthy. Investors had to file for these permits and additional licenses individually.
List of China Business License Requirements
● Unified social credit number
The unified social credit code comes along with the 5-in-1 business license. It’s an 18-digit set of numbers that can certify the company’s identification as a legally permitted business.
With this code, a business can easily transact with government offices, financial institutions, and other domestic companies within China. This requirement also improves brand credibility, making your company eligible for support programs and services launched by the local authorities.
● Business registration number
This requirement is the business license number you’ll acquire after the registration process. It’s not the company’s official identification but a number specifically released for your license. So, when the permit is lost or replaced, the business license number will also change.
● Official Company Name
A huge part of obtaining a Chinese business license is having a registered name in the local directory. Brands submitting Chinese company names must include which industry they belong to and the type of transactions they conduct in China.
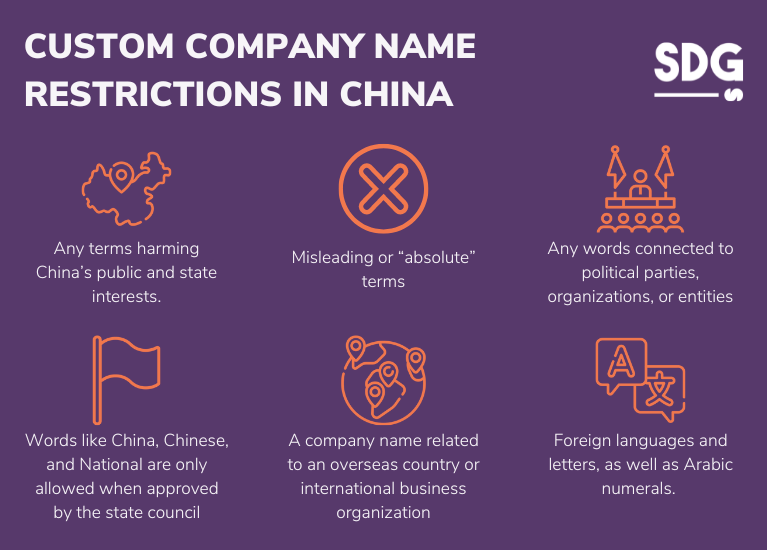
When coming up with a custom name, it’s important to note that there are certain restrictions you must follow. Here are some words you cannot include in your company name:
- Any terms harming China’s public and state interests.
- Misleading or “absolute” terms
- Any words connected to political parties, organizations, or entities
- Words like China, Chinese, and National are only allowed when approved by the state council
- A company name related to an overseas country or international business organization
- Foreign languages and letters, as well as Arabic numerals.
- Business or Company Type
When applying for a local license, you must also include a brief description of your business category. It should be mentioned in two to three words, like “咨询 (consulting company)”, “贸易 (trading)”, or “投资 (investment).”
These descriptions are only for identification. They do not restrict the business activities the company can undertake. For instance, a business listed as “trading” is not limited to only trading activities.
The type of the company should be indicated at the end of its name. Most foreign businesses entering the Chinese market opt for the Limited Liability Company (LLC).
Nevertheless, upon business license registration, a company’s trading name should follow the structure: Custom name + Business field + Company type.
- Legal representative
A legal representative serves as the official spokesperson for a company in legal matters. While every company possesses an official stamp used for authorization, the actions and signatures of the legal representative are regarded as decisions made by the company.
It’s important to note that the legal representative, being the face of the company, is held accountable if the company engages in any unlawful activities.
- Business scope
The business scope describes the company’s planned activities and transactions in the Chinese market. This requirement is more specific and descriptive than the industry and business category mentioned in the company’s trading name.
It’s crucial to ensure that all planned business activities are included in the business scope because conducting operations beyond this defined scope can lead to penalties from the government.
- Registered capital for the business
Every company must declare its registered capital, indicating the amount of money investors commit. Although there’s no legal minimum for registered capital, having an excessively low amount is generally discouraged.

This is because registered capital often reflects a company’s financial strength. A low registered capital could lead to potential business partners questioning the company’s stability and reliability.
This perception can significantly impact operations on major e-commerce online platforms like Tmall or Alibaba, which may have specific registered capital requirements.
- Establishment Date and Operating Period (Expiry Date)
When applying for a Chinese business license, it’s important to indicate the company’s official foundation date. On top of that, you’ll also need to provide the time frame for the operating period.
Once that period ends, the company must submit the required documents again, or the business will be dissolved.
- Registered Business Address
Each company must have a unique registered address before registering for a business license. However, if an office isn’t necessary to conduct your business activities, more cost-effective options are available through service providers.
Investors who are not ready to invest in a physical office space can opt for virtual office services. These provide an address for company registration but are unsuitable for daily operations or receiving mail, calls, or packages. However, virtual offices are more affordable than traditional office spaces.
How to get a business license in China?
With the digitalization of business license registration, companies can submit their application online. The system is backed by the State Administration for Industry and Commerce, allowing companies to submit application forms, requested documents, and e-signatures virtually.
Although this new process makes business license registration more convenient, the local bureaucracy can still appear complex for foreign companies and marketers. We highly recommend hiring a consulting company or agency to handle this procedure if you’re unfamiliar with the local systems or requirements.
Other requirements for getting a new business license in China include opening a bank account for the company. Depending on the company type, the process may also require you to submit a name list of directors and the identification card of the brand’s legal representative.
Wholly-foreign-owned enterprises should also present the company chops (a seal or stamp) and a detailed business plan approved by the Chinese government.
How much does it cost to register a business in China?
The costs of company registration in China, including the fees for a Chinese business license, vary depending on the enterprise’s type, size, and location.
In general, it can range anywhere between 30,000 RMB and 100,000 RMB or more. When computing these expenses, you have to consider the fees required by the government, as well as the legal and accounting service payments.
Can foreigners open a business in China?
Yes, foreign investors and entrepreneurs can open a business in China. In recent years, the Chinese market has eased with the entry restrictions for non-domestic businesses.
In fact, the Ministry of Commerce voiced its intention to provide a better business environment and policies for global investors in a statement released in October 2023. Based on the report, specific industries in China have eased foreign ownership restrictions, such as automobiles, banking, insurance, etc.
In general, foreign investors can choose between three options when establishing a company in China. The licensing requirements and process also depend on the business type they choose.

- Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise (WFOE)
A Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise (WFOE) is a type of limited liability company entirely owned and operated by foreign investors. Representing about 60% of foreign-owned businesses in China, WFOEs are the preferred structure for many leading multinationals, including Apple and Oracle.
- Sino-Foreign Cooperative Joint Ventures (JV)
A joint venture (JV) is a business arrangement where Chinese and foreign partners jointly invest, sharing ownership according to their contributions.
This model is popular among foreign businesses in China, with over 35% of the local market’s one million foreign enterprises operating as JVs. Well-known examples include SAIC Volkswagen and BMW Brilliance.
- Representative Offices (RO)
It’s a type of liaison office set up by foreign-invested enterprises in China to represent their parent company.
While ROs do not have the status of independent legal entities and cannot engage in direct business operations such as profit-making and remitting funds overseas, they are allowed to conduct non-commercial activities such as liaison, product promotion, market research, and bank account setup.
What are the benefits of obtaining a business license in China?
Securing a business license in China removes restrictions on foreign enterprises, providing you with complete control over your digital marketing strategies.
It’s especially vital if you operate an e-commerce or company website targeting the Chinese market, as it allows you to apply for an ICP license. This requirement is necessary for launching or hosting a localized website in China.
Top Challenges of Obtaining Chinese Business Licenses as a Foreign Company
1. Domestic Language Barriers
Language barriers present a considerable challenge, as most official documents, business records, and legal papers in China are in Mandarin or Simplified Chinese.
Misinterpretations or inaccuracies in translations can result in misunderstandings or incorrect evaluations of a company’s legitimacy, so it’s important to work with expert translators when undergoing these procedures.
2. Distinct Regulatory and Legal Framework
China’s distinct legal and regulatory environment adds complexity to verifying companies.
Business laws, corporate governance, financial reporting standards, tax regulations, and employment practices vary significantly from those in other regions. Newcomers to the Chinese market must stay informed about these regulatory updates.
3. Domestic and Non-centric Procedures
In contrast to some Western nations, which have centralized databases that make company data easily accessible, China’s records are dispersed across different regional and local government offices.
This scattered system makes the verification process lengthy and complex, with each step having distinct procedures and varying levels of efficiency.
Your Trusted Digital Marketing Partner in the Chinese Market!
While the requirements and procedures may appear daunting, obtaining a domestic business license presents many opportunities and perks for foreign companies. It’s a necessary process, especially for brands that intend to operate within the Chinese market in the long run.
You may also want to read:
Once you’ve secured your local license, Sekkei Digital Group can help you connect with Chinese consumers through proven and tested digital marketing strategies. With our extensive industry experience, we ensure that your brand stands tall amidst the competition in China’s fast-paced digital ecosystem.

Whether you need to localize your website or conduct market research for your brand, we have all the digital solutions you need. Contact us today, and let us start working together!
References:
All You Need To Know About Your Business License In China
Mastering China Company Verification: A Comprehensive Guide
Setting Up A Company In China: A Complete Guide
What is the China Business License: A Comprehensive Guide | 2024
China’s Five-in-One Business License



